Some experts heated the Cs0.33WO3 nanoparticles for thermal insulating glass in a carbon dioxide reducing atmosphere at different temperatures for 2 hours, and used the obtained powders to prepare transparent heat insulation films. After that, they observed the near-infrared shielding properties of the prepared thin film. The experts observed the transmittance spectra of Cs0.33WO3 films prepared before and after carbon powder atmosphere annealing at different temperature for 2h and found that:
More details, please visit:
http://cesium-tungsten-bronze.com/index.html
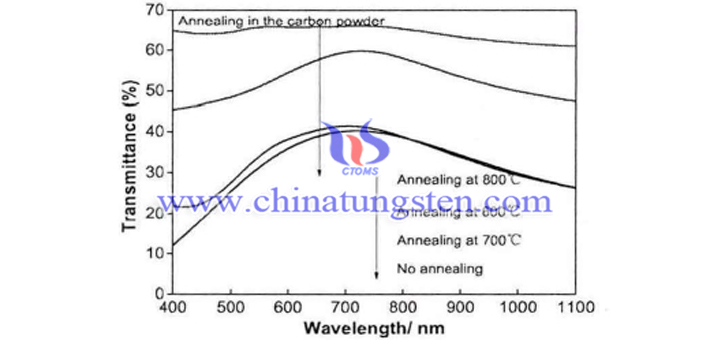
When heat treated at 600°C, the transmittance of the curve is significantly increased in the visible light and near-infrared regions, while the curve at 700°C is almost the same as the untreated powder curve. When the heat treatment temperature reaches 800°C, the light transmittance of powder in the visible light and near-infrared regions is almost the same. When the heat treatment temperature is 600°C, the required reducing atmosphere is insufficient and the transmittance is generally increased. At 800°C, although a certain reducing atmosphere is generated, the heat treatment temperature is too high. At the same time, the adhesion between the particles, the cohesive force is increased, the agglomeration is severe, and the particle size is seriously increased, so the shielding property of the prepared powder is lost in the near-infrared region.




